Understand the Working of Fiber Optic Cables
In today’s fast-paced digital world, information travels at breakneck speeds. But have you ever stopped to think about how this data gets from point A to point B? This is where the fiber optic cable comes in to help. These sleek, futuristic-looking cables are the backbone of the internet, carrying information across vast distances using the power of light.
But how exactly do optical fiber cables work? While traditional copper cables transmit electrical signals, optical fiber cables utilize light pulses to carry information. This allows for incredibly fast data transfer rates, making them the preferred choice for high-speed internet, long-distance communication networks, and even medical imaging.

Inside the Fiber Optic Cable:
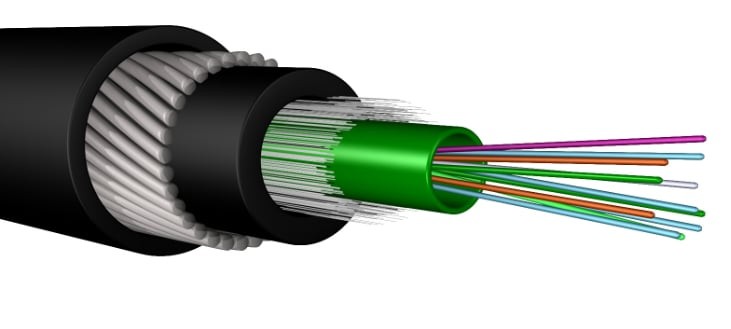
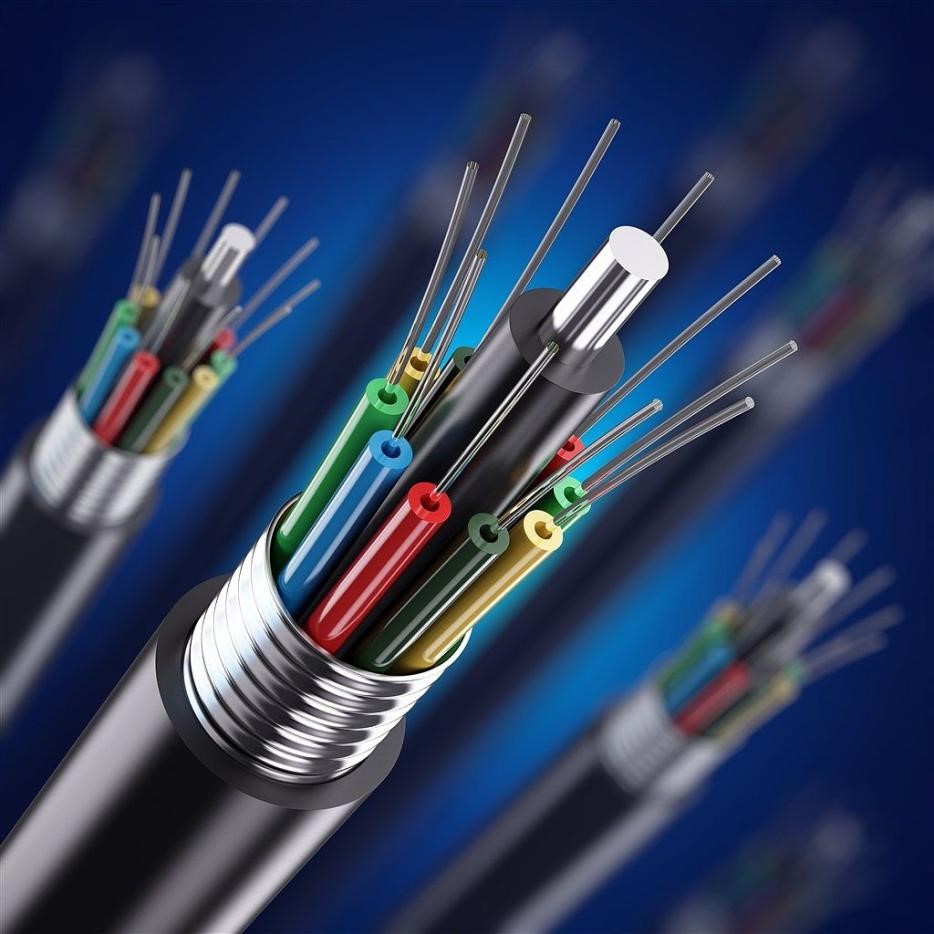
At its core, a fiber optic cable is a thin strand of glass or plastic, called a core, surrounded by a cladding layer made of a different material with a lower refractive index. This difference in refractive index plays a crucial role in how the light travels within the cable.
When a ray of light is traveling down the fiber optic cable, it hits the boundary between the core and the cladding, something fascinating happens. Due to the difference in refractive index, the light ray undergoes a phenomenon called total internal reflection. This essentially bends the light ray back into the core, preventing it from escaping the cable and traveling down its length in a series of zig-zag bounces.
Now, light itself doesn’t carry information. So, how do we encode data into these light pulses? Here’s where binary coding comes in. Binary code, the language of computers, uses a series of 1s and 0s to represent information. In fiber optic cables, the presence or absence of a light pulse can represent these binary digits.
- On (1): A light pulse is transmitted down the cable core.
- Off (0): No light pulse is transmitted.
By rapidly turning the light source on and off, we can send digital information as a stream of light pulses through the fiber optic cable.
At the receiving end of the fiber optic cable, a photodetector converts the light pulses back into electrical signals. These electrical signals can then be interpreted by the receiving device, allowing the information to be retrieved.

Applications of Optical fiber cables:
Optical fiber cables find utility in a diverse array of applications.
- Internet: Optical fiber cables form the backbone of the Internet, facilitating high-speed data transfer for homes and businesses.
- Telecommunications: These cables are vital for long-distance phone calls, video conferencing, and other telecommunication services.
- Medical Imaging: They are used in medical equipment like endoscopes and MRI machines for high-resolution imaging.
- Data Centers: Optical fiber cables connect servers within data centers, enabling fast and reliable data storage and retrieval.

As our reliance on data increases, so does the demand for faster and more reliable communication networks. Optical fiber cables, with their superior speed, distance, and security capabilities, are perfectly positioned to meet these demands. Their importance in the digital world is undeniable, and they will undoubtedly continue to play a vital role in shaping the future of information transmission.
If you are looking for high-quality optical fiber cables for your specific needs, then OMC Cable is the right place for you. We offer a wide range of fiber optic cable solutions to cater to your unique requirements. Please feel free to contact us today to learn more about our fiber optic cable solutions and their pricing.